How Does Your Smartwatch Detect Heartbeats on a Wall or Fruit?
Have you ever worn your smartwatch on a wall or fruit, and to your amazement, it started detecting heartbeats? Of course, this can be confusing because walls and fruits don’t have a pulse. So, how does a smartwatch manage to read heartbeats from surfaces that don’t have any? To understand this, we need to explore the amazing technology that powers heart rate detection in smartwatches.
In this article, we will dive deep into how smartwatches work, what technology enables them to measure heartbeats, and why sometimes they appear to detect pulses from seemingly lifeless objects. So, if you’re curious about the inner workings of your smartwatch and the heart rate monitoring feature, keep reading!
How Smartwatches Detect Heartbeats
Smartwatches are equipped with sensors that are designed to detect and monitor your heart rate. These sensors are not just basic elements but work through advanced technology that allows them to detect subtle changes in blood flow. The most common method used in smartwatches for heart rate monitoring is called Phot plethysmography (PPG).
Phot plethysmography (PPG): The Key to Heart Rate Detection
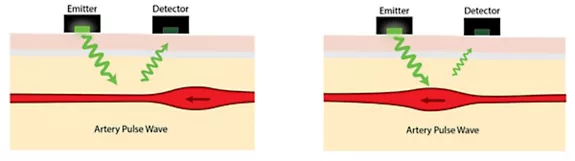
PPG is a non-invasive optical technique based on the detection of light changes in blood volume. The process works by emitting light into the skin, and the reflected light is then reflected back to the sensor. When your heart beats, the blood vessels expand and contract, changing the amount of blood flowing through your skin. These changes in blood volume affect the amount of light that is reflected back to the sensor.
The smartwatch uses this reflected light to measure the rate at which your blood volume changes, which directly correlates with your heartbeat. This data is then processed by the internal algorithms of the smartwatch to calculate your heart rate.
Why Does the Smartwatch Detect a Heartbeat on Non-Living Surfaces?
Now that we know how heart rate detection works, let’s look into why your smartwatch might register a heartbeat when placed on a wall or fruit.
1. The Sensor’s Sensitivity
One of the reasons for this anomaly is the extreme sensitivity of the sensor. The PPG sensor in your smartwatch is finely tuned to detect even the smallest variations in light reflection. When you put the smart watch on a wall or fruits, it can sense minuscule movements caused by your environment. For example, walls or fruits reflect light in diverse ways based on the surface features, moisture levels, or even shapes, and these might trigger an incorrect reading.
2. External Interference
The smartwatches are very sensitive devices, and their sensors can pick on ambient vibrations or changes in the environment. For instance, the natural vibration that results from movement of the air or objects nearby can make the sensor think it has detected a heartbeat. This usually occurs when the surface is moving or under slight pressure.
3. Moisture and Texture of the Fruit
Fruits, especially those water-rich like apples, oranges, or grapes, may interfere with the light coming from the sensors on the smartwatch. If used on the fruit, moisture and fruit texture can cause light to behave in ways that are reflective of the variations during the heartbeat. The smartwatch might interpret this as its pulse, although fruits obviously do not have a heart that beats.
4. Surface of the Wall; Temperature
Walls, depending on the material, may also interfere with the light sensor of the smartwatch. If the wall is warm or cool, or if it has imperfections in its texture, it might change how the light reflects back to the sensor. Walls, though they don’t have a pulse, might create patterns in the data of the sensor that are mistaken for heartbeats.
How Smartwatch Sensors Are Designed to Work
Smartwatches today are designed to deliver accurate heart rate measurements in normal conditions. They have been engineered with multiple sensors, such as:
PPG Sensors: As discussed above, they make use of light to capture the change in blood flow.
Accelerometers: These sensors measure movement and vibrations, which help the watch determine if you’re moving, exercising, or if the watch is resting.
Gyroscope: This detects the orientation of the watch and can determine whether it is on a flat surface or on your wrist.
Together, these sensors enable the smartwatch to produce accurate and meaningful data. Although the PPG sensor is primarily the one responsible for detecting heart rate, the accelerometer and gyroscope help improve its accuracy by confirming that the device is in the right position to measure your pulse-your wrist.
Why Does This Matter?
It is essential to note that the heartbeat detected by your smartwatch when placed on non-living objects does not necessarily mean there is a biological pulse. It rather indicates an environmental factor or sensor sensitivity.
This is also a reminder of how far wearable technology has come. Even if your smartwatch sometimes gives you false readings on certain surfaces, it’s still an impressive piece of technology designed to measure your health metrics with impressive precision.
How to Get Accurate Heart Rate Readings
To get the most accurate heart rate readings from your smartwatch, make sure to wear it correctly:
Wear it tightly: The watch should be fitted snugly, but not so tight that it is uncomfortable. The sensor won’t get a reading if the watch is too loose.
Keep it in the right place: Wear your smartwatch on the inner side of your wrist, just above the bone where blood flows well for measuring.
Avoid moving excessively: If you’re exercising or moving too much, it can cause erratic readings. Resting will help your smartwatch get a more accurate heart rate reading.
The Future of Heart Rate Monitoring in Wearables
Smartwatch technology is constantly evolving. Manufacturers are continuously working on improving the sensors to provide even more accurate readings. In the near future, we may see wearables that offer more advanced health monitoring features, such as blood oxygen levels, ECG (electrocardiogram) measurements, and even stress tracking.
As technology continues to advance, smartwatches will become even more capable of providing real-time insights into your health. The sensors in these devices will get better at filtering out false readings from external surfaces, allowing them to give you the most accurate data possible.
Conclusion
While it may seem amazing for your smartwatch to capture a heartbeat on an apple or the wall, that is actually just a result of technology and the way sensors are applied. The advanced photoplethysmography that your smartwatch uses is a very powerful health monitoring tool, but sometimes this equipment picks up false readings due to surfaces reacting with light in unpredictable ways.
As wearables get smarter and more advanced, you can expect even more precise heart rate monitoring and health tracking features. Whether you are using your smartwatch for fitness or medical reasons, understanding how it works will help you make the most out of its features.
Remember, the best way to read an accurate heart rate measurement is to have your smartwatch correctly fitted on the wrist and in a stable position. With that in mind, use your smartwatch’s features responsibly and keep using it to monitor your health!
For more Blogs visit out Blog Page







